Housing insulation essential
for CO2 reduction
*Source: "Comfortable and Healthy Homes with Energy-Saving Building Materials," Center for the Dissemination and Promotion of Energy Efficient Construction Materials, Japan Construction Material and Housing Equipment Industries Federation
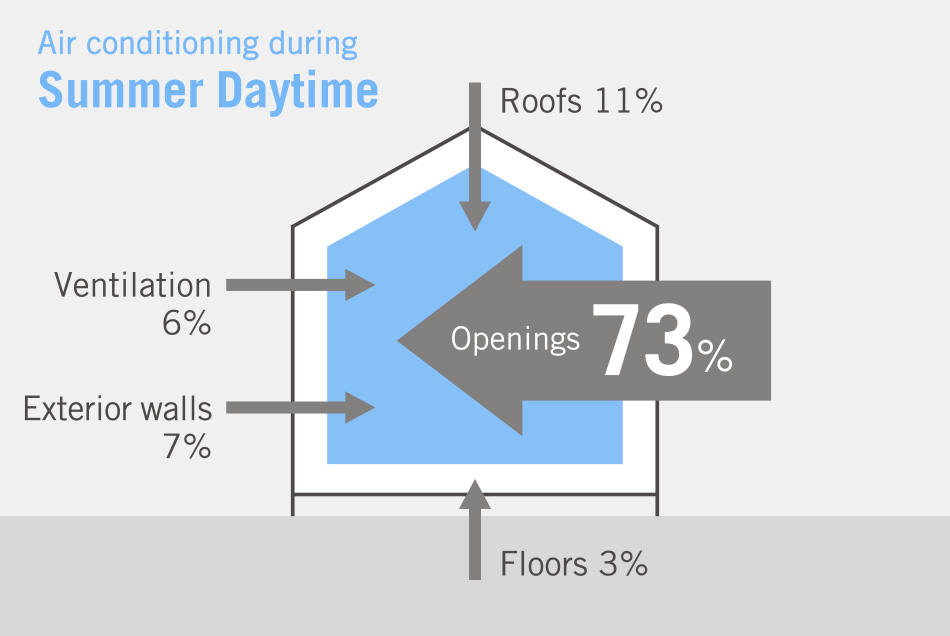
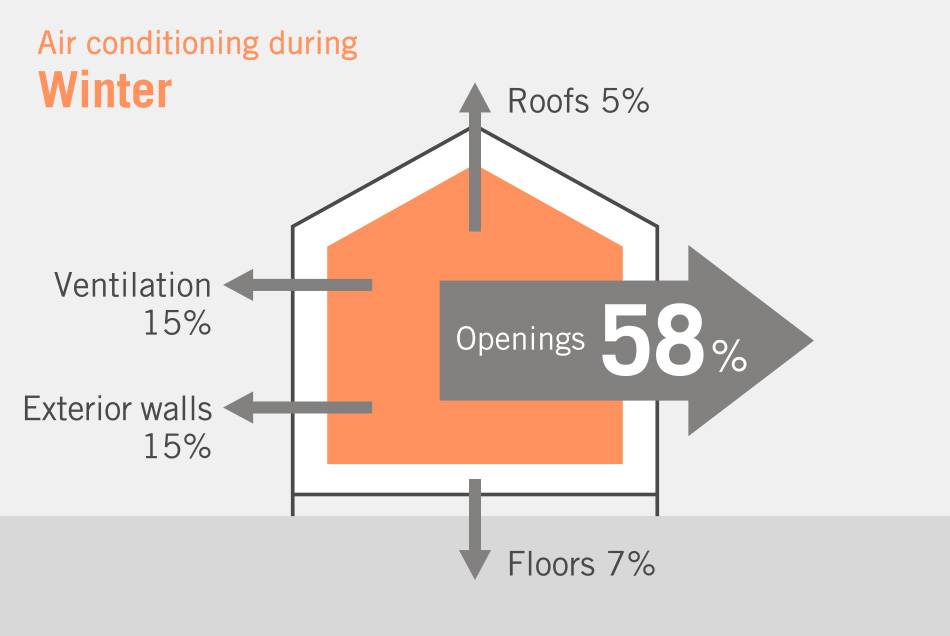
The largest component of energy consumption—and source of CO2 emissions—in the household sector is heating in winter and cooling in summer. Improving the thermal insulation of housing is therefore key to reducing CO2 emissions. By improving the insulating efficiency of window and door openings—places where energy loss is especially high—the energy required for heating and cooling can be dramatically reduced.
Improved performance required for both new and existing housing
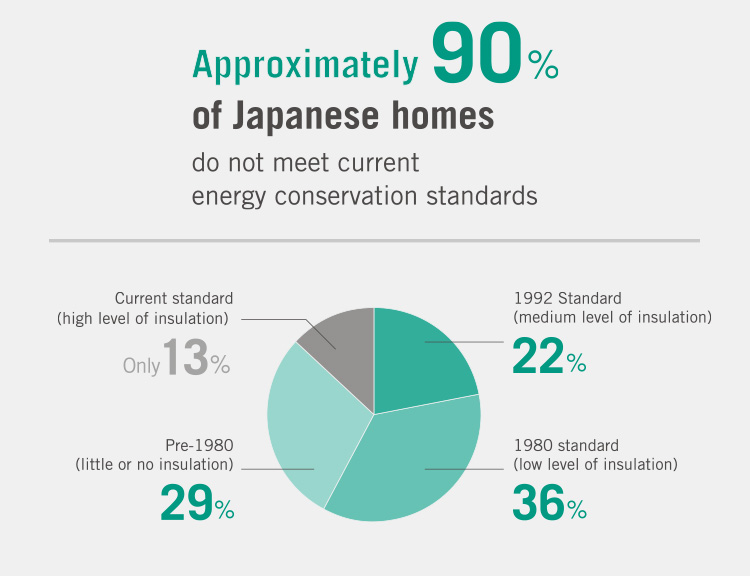
Given Japan's huge stock of existing homes, it is critical to improve the efficiency not only of new housing but also of existing stock. Japan lags behind other countries in the development of high-performance housing, with one survey showing that some 90%* of homes do not meet even current energy conservation standards. To substantially reduce greenhouse gas emissions in the household sector, the insulation performance of both new and existing homes must be improved.
*Source: Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism, 2021, Building Subcommittee, Council for Social Infrastructure Development
Triple glazing unit significantly
improves home insulation
With so much household energy loss attributable to the poor thermal insulation of window openings, window design plays a major role in reducing the carbon footprint of houses. Heat loss can be significantly reduced by replacing standard windows for ones with better insulating performance. For example, replacing single-glazed windows with double-glazed windows can reduce heat loss by approximately 50%, while triple-glazed windows can reduce heat loss by approximately 60%. Calculations show that replacing single-glazed windows in new and existing homes with triple-glazed high-performance windows that reduce heat loss by up to 80% would result in a significant reduction in CO2 emissions.
Calculation Method:•New construction: Assuming all windows (18 windows) are replaced with hybrid sash + triple-glazed windows •Remodeling: Assuming nine windows in the living room are replaced with hybrid sash + triple-glazed windows •Assuming that a representative area in terms of energy conservation would be Area 6 in the standard classification, and assuming a standard house as given in "Design Guidelines for Self-Sustaining Circulation Housing"*Figures may vary depending on the size of house, floor plan, equipment, and geographic region.
Tostem's products for
insulating home openings
TOSTEM’s lineup of products increase the energy efficiency of homes by improving the insulation at window and door openings where heat can easily escape. By dramatically improving the insulating properties at openings, we are contributing to the shift towards carbon-neutral housing in Japan.
Windows for remodeling
INPLUS *4
Contribution to
CO2 reduction
335kg-CO2/year
Savings
22,457yen/year
*4 Effect of adding INPLUS Low-E double-glazing glass (clear with argon gas) to 9 of the 18 aluminum sash single-glazed windows in a living room. Calculations for entrance doors are made based on aluminum specifications.
Windows for remodeling
REPLUS *5
Contribution to
CO2 reduction
281kg-CO2/year
Savings
18,838yen/year
*5 Effect of replacing REPLUS Low-E double-glazing glass (clear with argon gas) to 9 of the 18 aluminum sash single-glazed windows in a living room. Calculations for entrance doors are made based on aluminum specifications.
Entrance door for remodeling
Rechent3 *6
Contribution to
CO2 reduction
14kg-CO2/year
Savings
944yen/year
*6 Effect of Rechent3 high insulation specification with daylighting. Calculated by aligning windows with aluminum sashes and single-glazing.
Basis for calculation of CO2 reduction and amount saved per product (Japanese only)